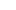How do medical trocars help reduce trauma in abdominal surgery?
Abdominal surgery is one of the common medical treatment methods, widely used in the treatment of various abdominal diseases, such as cholecystitis, appendicitis, and intestinal obstruction. Traditional open surgery usually requires a large incision, which not only causes significant trauma and requires a long recovery time, but also may be associated with a higher risk of complications. With the development of minimally invasive technology, laparoscopic surgery has become an ideal option, performing surgery through small incisions, reducing trauma, and promoting postoperative recovery.
In laparoscopic surgery, the medical trocar, as a key tool, plays a crucial role. This article will introduce you to the function and role of medical trocars, explaining how they effectively reduce trauma in abdominal surgery and provide a safer and more efficient surgical process.
1. Basic Structure and Function of Medical Trocars
A medical trocar, also known as a laparoscopic trocar, is a medical device used to establish a channel for laparoscopic surgery. Its basic components include:
Puncture needle: Used to penetrate the abdominal wall and create a channel into the abdominal cavity. The puncture needle usually has high hardness and sharpness, allowing it to safely penetrate the skin and abdominal wall.
Cannula: The cannula is usually made of metal or plastic and is cylindrical in shape. After insertion into the abdominal wall, it maintains the patency of the channel and provides access for the laparoscope camera, surgical instruments, etc. The inner lumen of the cannula is smooth, preventing damage to the abdominal wall tissue during instrument insertion.
Gas insufflation channel: The cannula usually also has a gas insufflation channel, through which carbon dioxide gas can be injected to create a pneumoperitoneum in the abdominal cavity, providing the necessary working space.
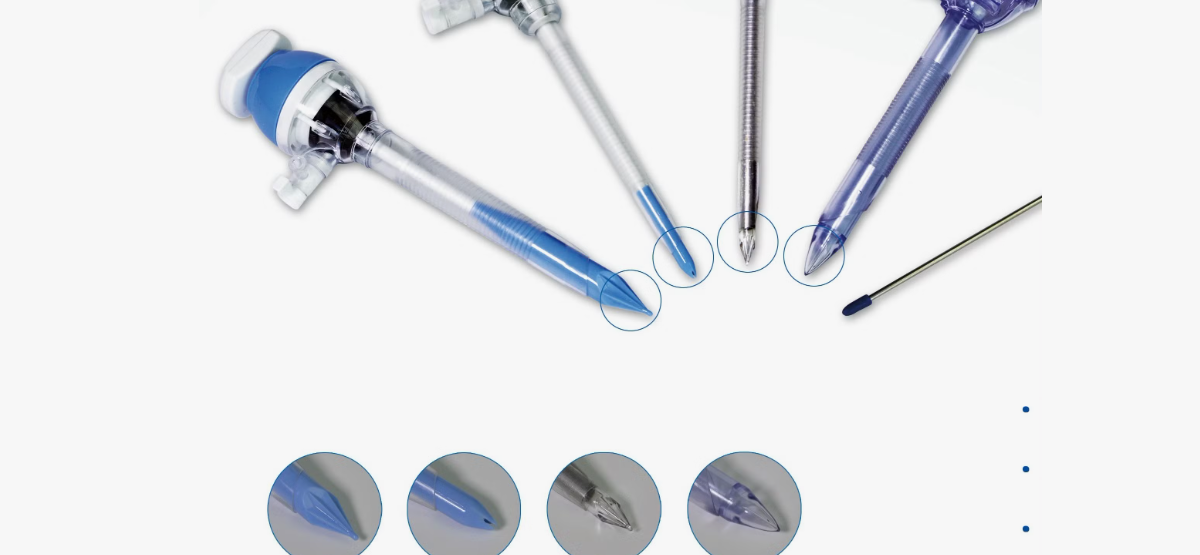
2. How Medical Trocars Reduce Trauma in Abdominal Surgery
The role of medical trocars in laparoscopic surgery is not only to provide a surgical channel, but more importantly, to help reduce trauma in abdominal surgery through the following aspects:
(1) Reducing the size of the surgical incision
Traditional open abdominal surgery requires a large incision to perform abdominal procedures. This not only causes significant trauma but also requires a longer recovery time, and patients may need more time to fully recover after surgery. In contrast, laparoscopic surgery typically involves inserting medical trocars through several small incisions, which are usually only a few millimeters wide. Because the trauma caused by the trocar during insertion is minimal, and the trocar maintains a clear passage, postoperative pain and recovery time are significantly reduced.
(2) Reduced damage to intra-abdominal tissues
In traditional surgery, due to the need to expose a large area of the abdominal cavity, it is easy to damage the organs and tissues within the abdominal cavity during the surgical process. When performing laparoscopic surgery using medical trocars, surgical instruments enter through small incisions, eliminating the need for extensive exposure of the abdominal organs, allowing for more precise manipulation, and thus reducing interference with and damage to surrounding tissues. The trocar itself is designed for precise penetration, avoiding the risk of accidental injury to organs.
(3) Reduced intraoperative bleeding and complications
Because laparoscopic surgery involves smaller incisions and requires less operating space, it typically does not involve the extensive tissue dissection and exposure seen in open surgery. Therefore, when using medical trocars for laparoscopic surgery, intraoperative bleeding is usually less, wound healing is faster, and the risk of postoperative complications such as infection is relatively lower. The trocar helps the doctor perform surgery under clear visualization, further reducing the risks during surgical procedures.
(4) Providing stable pneumoperitoneum pressure
In laparoscopic surgery, carbon dioxide gas is injected into the abdominal cavity through a medical trocar to create a pneumoperitoneum. The pneumoperitoneum keeps the abdominal organs at an appropriate distance from the abdominal wall, providing a clearer view and more surgical space. This not only increases the operating space but also allows the doctor to perform the surgery more precisely, reducing operational errors and tissue damage caused by insufficient space.
Formation of pneumoperitoneum: After carbon dioxide gas is injected into the abdominal cavity, it forces the volume of the abdominal cavity to increase, making the internal organs more clearly visible, facilitating the doctor's operation.
Pressure control: The pressure of the pneumoperitoneum needs to be precisely controlled; excessively high pressure may have adverse effects on internal organs, while excessively low pressure will affect the field of view and surgical space. Therefore, modern medical trocars are usually equipped with a pressure regulation system to ensure the stability of the pneumoperitoneum.
(5) Shorter Postoperative Recovery Time
Due to the minimally invasive nature of laparoscopic surgery and less tissue disruption, patients experience significantly shorter postoperative recovery times. Patients undergoing surgery with medical trocars can usually resume normal activities in a shorter period after surgery, reducing hospitalization time and recovery period. Compared to traditional open surgery, laparoscopic surgery results in smaller scars and less postoperative pain, helping patients return to their daily lives and work more quickly.
3. Other Advantages of Medical Trocars
In addition to reducing surgical trauma, the use of medical trocars in laparoscopic surgery offers other important advantages:
Improved Surgical Field of View: Laparoscopic surgery involves small incisions, allowing for the direct introduction of a high-definition camera into the abdominal cavity. Doctors can see the internal conditions of the abdominal cavity in real-time on a monitor. This allows doctors to more clearly locate the lesion site, ensuring the accuracy of the surgery.
Improved Operational Precision: Through laparoscopic surgery, doctors can use video images and advanced surgical instruments for precise excision or repair, reducing the possibility of errors.
Lower Hospitalization Costs: Due to shorter recovery times, patients can be discharged sooner, thus reducing hospitalization costs and alleviating the financial burden on patients.
Medical trocars not only help doctors complete surgery by providing a stable working channel and clear vision, but also effectively reduce surgical trauma, shorten recovery time, and lower surgical risks.



 English
English Español
Español Français
Français










 CONTACT US
CONTACT US