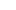WHAT WE DO
We prioritize the well-being and comfort of our patients,offering
personalized treatments and a supportive
Medical Device Solutions
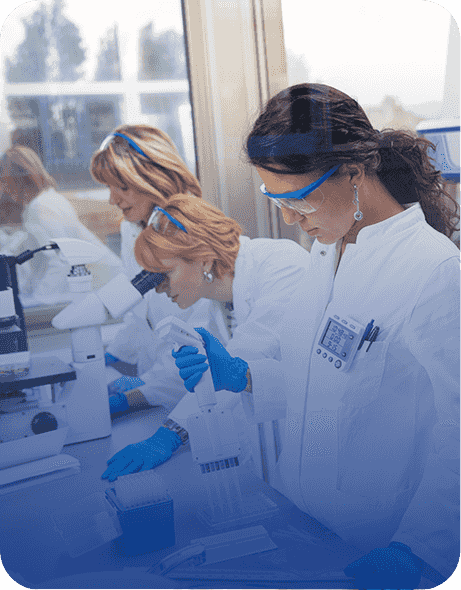
Eray has established a comprehensive quality control system that encompasses the entire production process, including testing and traceability, from the ISO Class 8 cleanroom to a partial ISO Class 6 physical and chemical laboratory, ensuring that every customer receives trustworthy products.
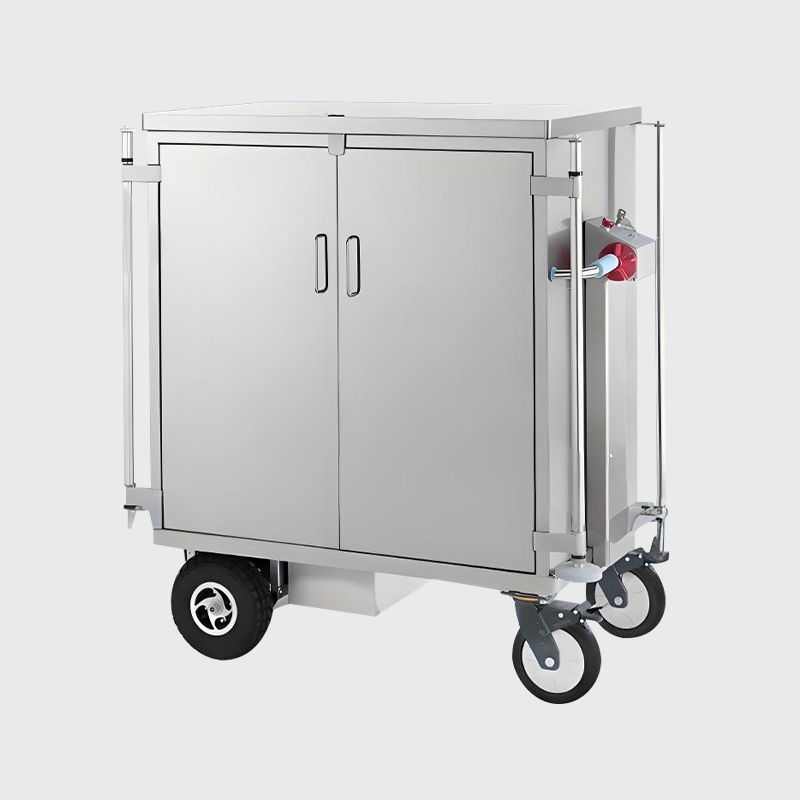
Ward Care
We prioritize the well-being and comfort of our patients, offering personalized treatments and a supportive.
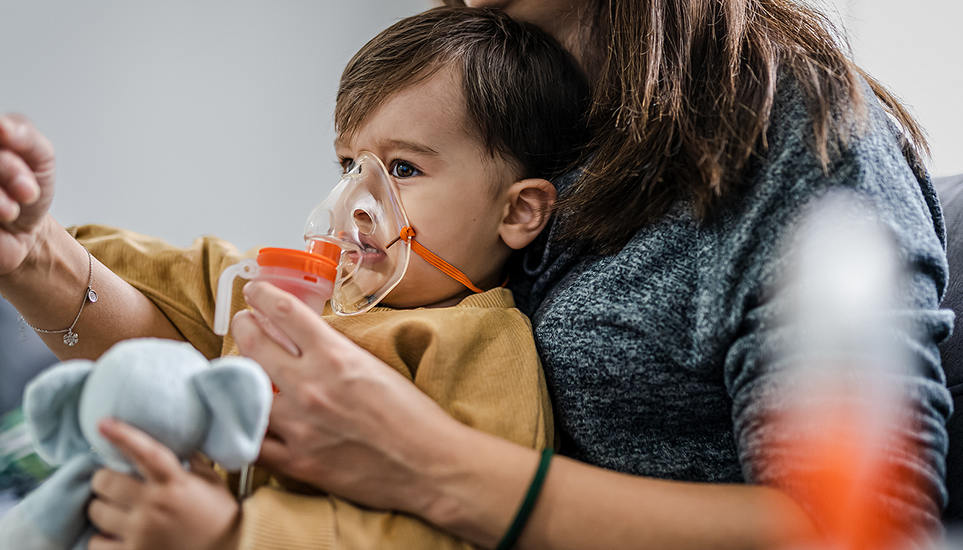
Respiratory Therapy
For the ICU, emergency department, and chronic respiratory disease management.
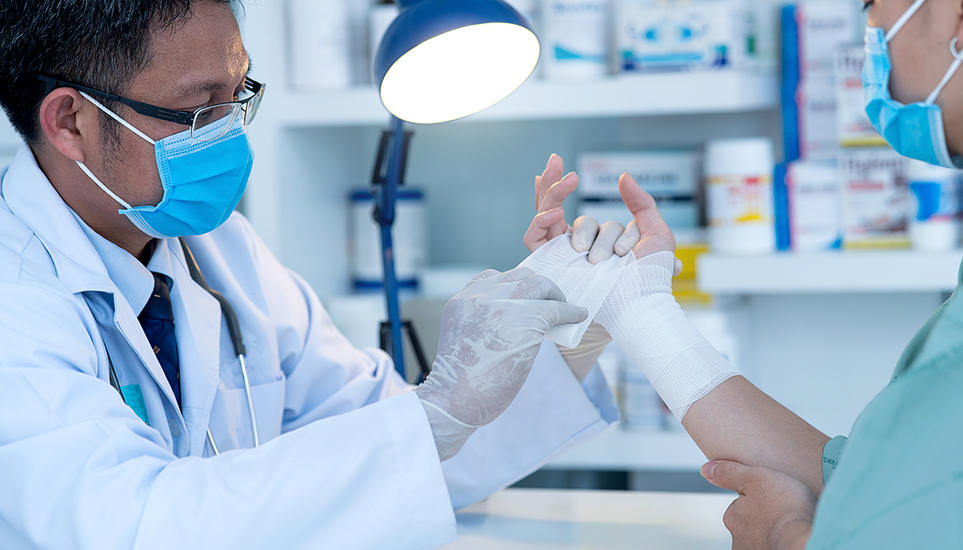
Sterilisation Monitoring
For the central supply room (CSSD), operating theatre instrument sterilisation control, etc.
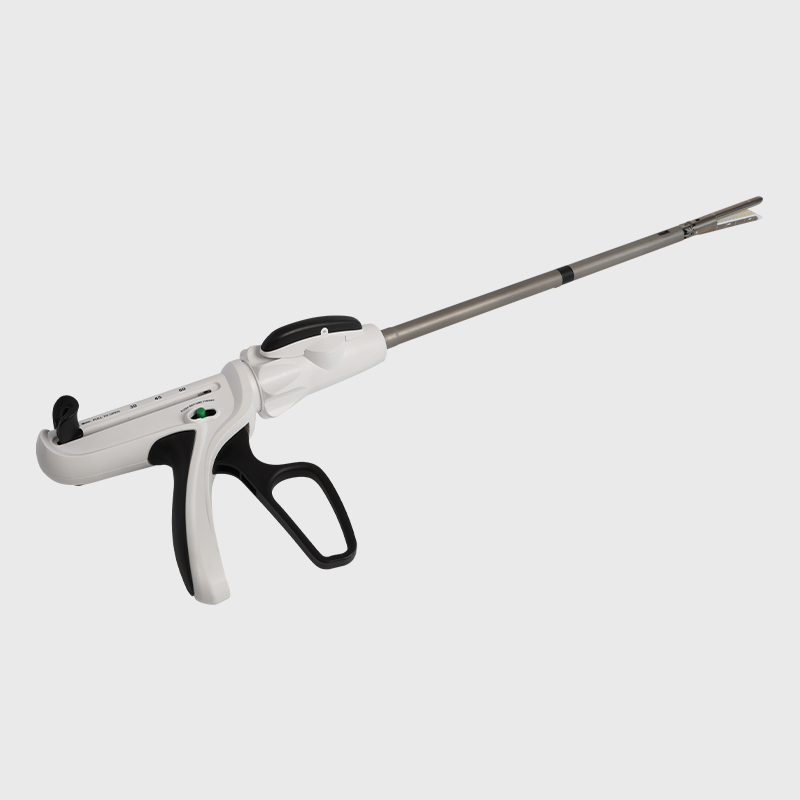
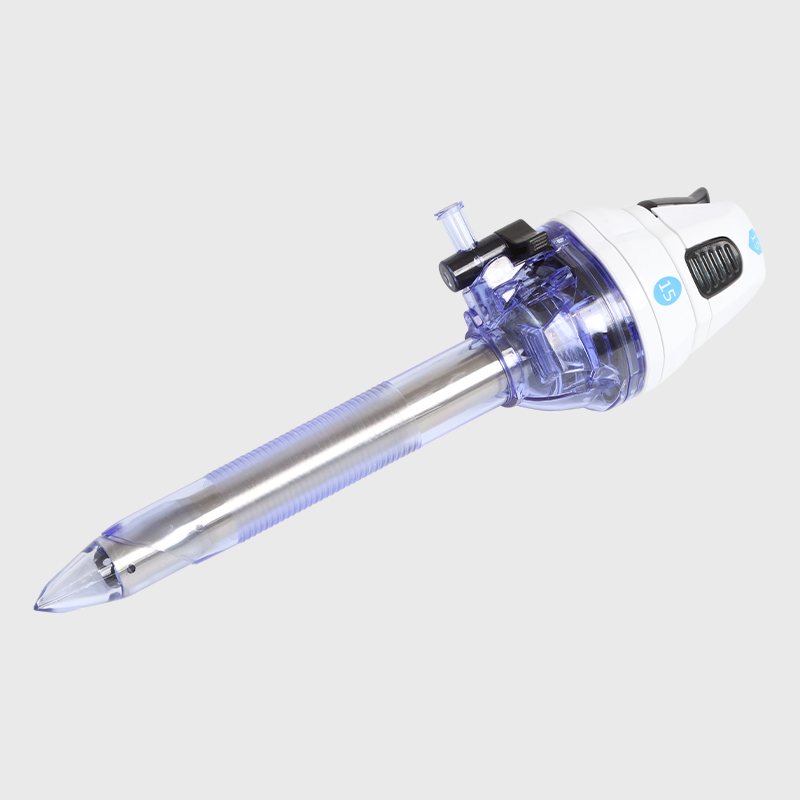
Minimally Invasive Surgery
For laparoscopy, ligation, anastomosis, and other minimally invasive surgery.

-
0m2
Company Area
-
0
Founded In
-
0
Employees
-
0
Cooperative Customer
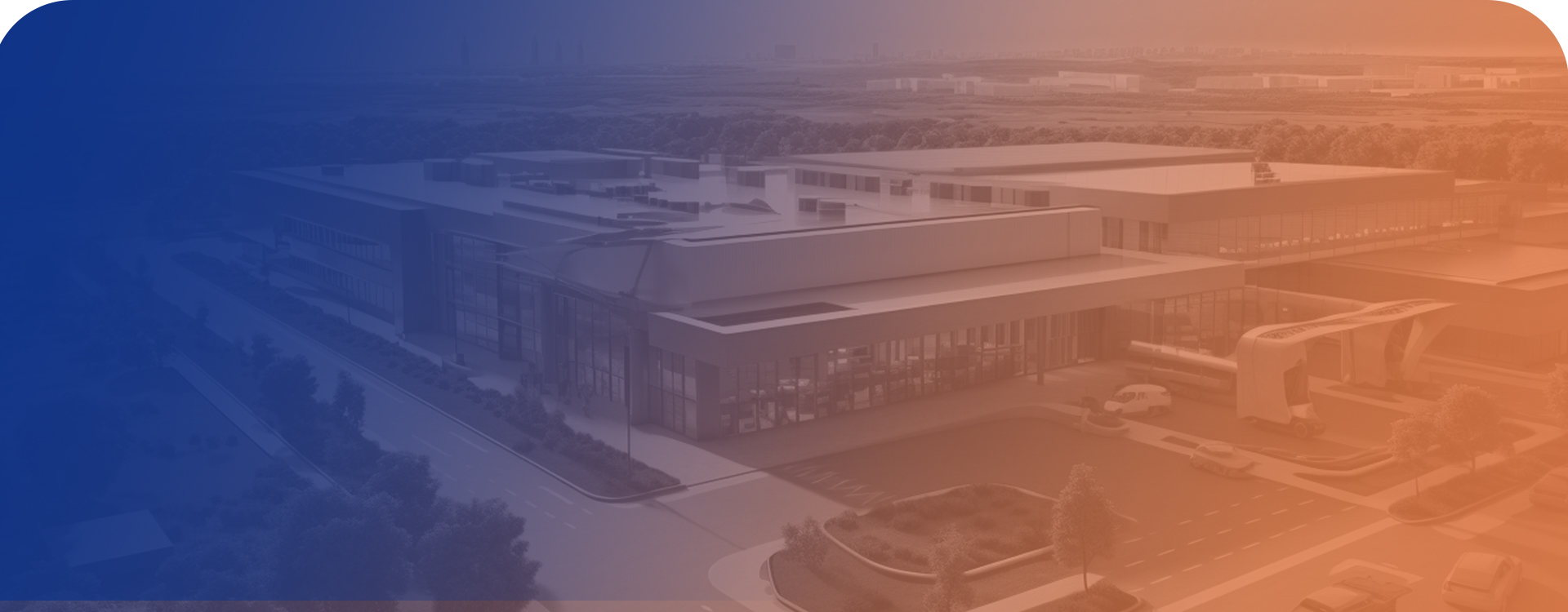
ERAY HAS BUILT THE WHOLE PROCESS OF PRODUCTION, TESTING AND TRACEABILITY
Eray Medical Technology (Nantong) Co., LTD., is a medical device manufacturing enterprise
integrating research and development, production, and sales. The company is located in Rudong
Economic Development Zone, adjacent to Shanghai, with convenient transportation, and
developed information. As a professional
VIEW MORE
medical devices manufacturers and medical consumables factory
, The company covers an area of 70 mu, with a construction area of 20310 square meters. It has an ISO Class 8 cleanroom, an ISO Class 7 microbiological laboratory, and a partial ISO Class 6 physical and chemical laboratory.ERAY
TRUSTED AUTHORITATIVE
CERTIFICATE
Eray has passed ISO 13485, CE and other international certifications. We have also obtained FDA registration for some of our products, and have established a complete quality traceability and verification system. We believe that stable and reliable products come from adherence to standards.
WHAT’S NEWS
-
Industry NewsJan 08 ,26
-
Industry NewsJan 01 ,26
-
Industry NewsDec 23 ,25
-
Industry NewsDec 16 ,25
-
Industry NewsDec 09 ,25
-
Industry NewsDec 02 ,25



 English
English Español
Español Français
Français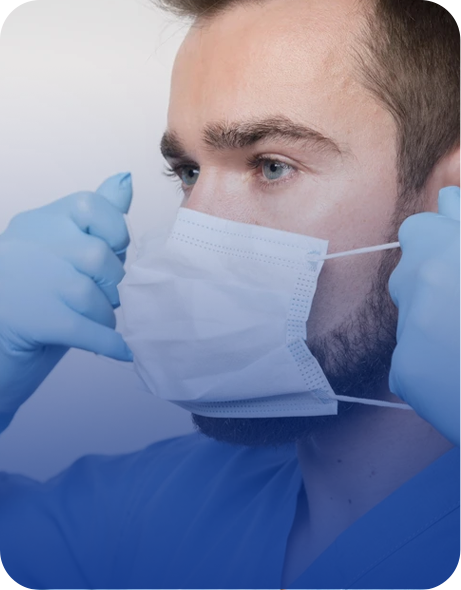












 CONTACT US
CONTACT US