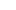What is the correct way to use wound dressings?
Wound dressings play a crucial role in wound care, effectively protecting wounds, preventing infection, and accelerating healing. However, only by using wound dressings correctly can their effectiveness be maximized. Different types of wounds, different dressing materials, and different situations require different care methods.
1. Choosing the right wound dressing
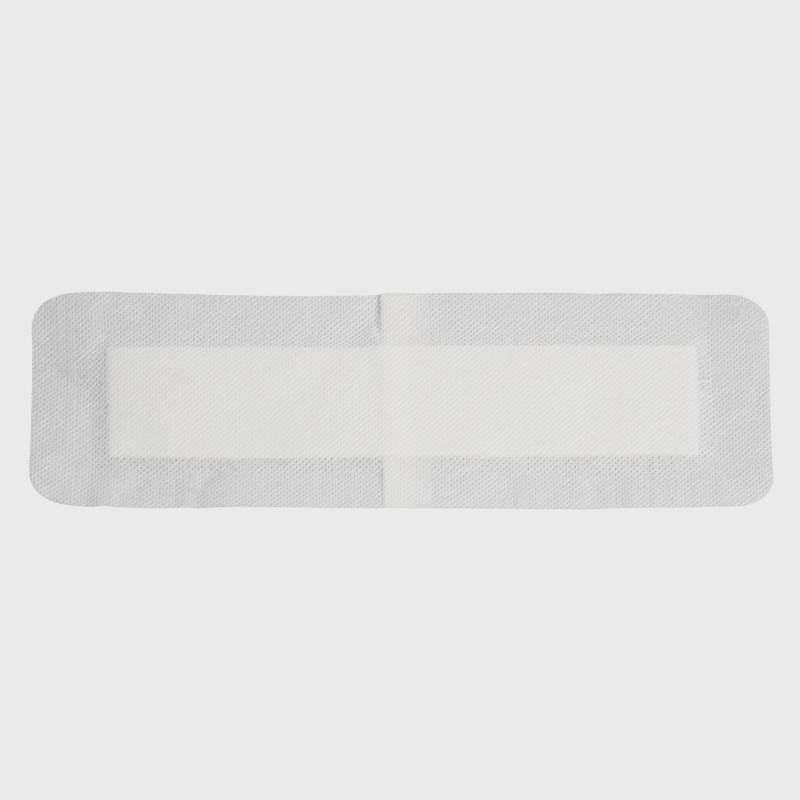
There are many types of wound dressings available on the market, including gauze dressings, adhesive bandages, breathable dressings, moist dressings, and absorbent dressings. Choosing the right dressing provides the best protection and healing environment for the wound.
When choosing a wound dressing, consider the following factors:
Wound type: Different wounds require different types of dressings. For example, superficial scratches or small incisions can use adhesive bandages, while larger or deeper wounds require moist dressings or absorbent dressings to keep the wound moist and promote healing.
Wound Exudation: If there is significant wound exudation, choose a highly absorbent dressing, such as a foam dressing or a moisture-wicking dressing, to prevent further exudation and reduce the risk of infection.
Wound Infection Risk: For wounds with a high risk of infection, use antibacterial dressings, such as silver ion dressings or dressings containing antibacterial ingredients, to effectively prevent infection.
Patient Allergy History: Choose dressings without allergens to avoid allergic reactions.
2. Correct Procedures for Using Wound Dressings
Correct procedures for using wound dressings not only protect the wound but also accelerate healing and reduce complications. The following are the standard procedures for using wound dressings:
(1) Cleaning the Wound
Before applying a wound dressing, the wound must first be cleaned. This is a crucial step in ensuring wound healing and preventing infection. Gently clean the wound with saline or a specialized wound cleansing solution to remove dirt, bacteria, or other impurities from the wound surface. Avoid direct contact of alcohol or iodine with the wound, as they may irritate the wound and affect healing.
(2) Disinfect Hands and Dressings
Before handling the wound and dressings, thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water, or disinfect them with a hand sanitizer. When opening the packaged wound dressing, ensure it remains sterile to prevent contamination by external bacteria.
(3) Apply Ointment or Disinfectant (If Needed)
If the wound requires medication (such as an antibacterial ointment), apply a thin layer of ointment or disinfectant to the wound surface. Medication helps control the risk of infection, but should be used only as advised by your doctor.
(4) Cover with Dressing
Gently place an appropriately sized wound dressing over the wound. The dressing should not be too large or too small, ensuring it completely covers the area around the wound, but avoid dressings that are too large and cause discomfort. For deeper wounds, sponge or foam dressings can be used, as they absorb exudate and keep the wound moist.
(5) Secure the Dressing
The dressing usually needs to be secured with bandages, tape, or a special securing strap. Avoid securing it too tightly to prevent restricting blood circulation. The fixed dressing should fit the wound snugly but not compress it, ensuring the wound can heal in a sterile environment.
(6) Dressing Changes
Wound dressings need to be changed regularly to ensure the wound remains clean and dry. Generally, the dressing change frequency depends on the size and type of the wound. For small wounds or wounds with low exudate, dressings should be changed every 2-3 days; for large wounds or wounds with significant exudate, dressings should be changed every 24 hours as advised by a doctor.
3. Precautions for Using Wound Dressings
Avoid Excessive Friction: Dressings should not be used to rub the wound for extended periods to prevent the wound from becoming larger or deeper, causing infection or delayed healing.
Keep Dry and Ventilated: Wound dressings should be kept dry and ventilated to prevent excessive moisture from promoting bacterial growth and affecting healing.
Observe Wound Changes: Regularly check the wound's healing progress. If signs of infection appear, such as redness, swelling, fever, or increased exudate, seek medical attention promptly.
Avoid Unnecessary Dressing Removal: During wound healing, avoid unnecessarily removing or prematurely changing the dressing to prevent disrupting the wound's healing environment.
Proper use of wound dressings can effectively prevent infection, reduce pain, and promote rapid wound healing. When using wound dressings, we should select the appropriate dressing based on the wound type and amount of exudate, and follow the correct application steps to ensure the dressing's sterility and safety. At the same time, we should regularly check the wound's healing progress and change the dressing promptly to ensure optimal healing conditions.



 English
English Español
Español Français
Français










 CONTACT US
CONTACT US