How effective is a steam sterilizer?
The sterilization effect of steam sterilizer (also known as high-pressure steam sterilizer) is one of the most reliable and widely used sterilization methods, especially in the medical, laboratory and industrial fields. Its sterilization effect mainly depends on the penetration and thermal stability of high-temperature saturated steam, which can effectively kill all microorganisms including bacteria, viruses, fungi and spores.
Content
1. Sterilization principle and advantages
The sterilization effect of steam sterilizer mainly depends on the synergistic effect of high-temperature saturated steam. In a closed high-pressure environment, steam can quickly penetrate the surfaces and pores of the sterilized items, destroying the protein, nucleic acid and cell membrane structure of the microorganisms and making them inactive.
(1) Scientific ratio of temperature and time
Standard sterilization conditions: 121℃ for 15~30 minutes, or 134℃ for 3~10 minutes.
High temperature (≥121℃) can quickly kill common bacteria and viruses, while heat-resistant spores (such as anthrax spores) require a longer action time.
(2) High pressure enhances penetration
The working pressure is usually 0.1~0.2MPa (1~2 atmospheres). The high pressure environment enables steam to penetrate into the complex structure of the instrument (such as lumen, joint gap), ensuring sterilization without dead angles.
(3) Broad-spectrum sterilization ability
It can inactivate tuberculosis, hepatitis B virus (HBV), HIV and stubborn bacterial spores (such as Clostridium spores), which is impossible for many other sterilization methods (such as ultraviolet light and alcohol disinfection).
2. Verification method of sterilization effect
To ensure the effectiveness of the sterilization process, it must be verified by physical, chemical and biological triple monitoring means:
(1) Physical monitoring
The built-in sensor of the sterilizer records the temperature, pressure and time curves in real time to ensure that the actual parameters meet the set values (such as 121℃ for 15 minutes). Any deviation may lead to sterilization failure.
(2) Chemical monitoring
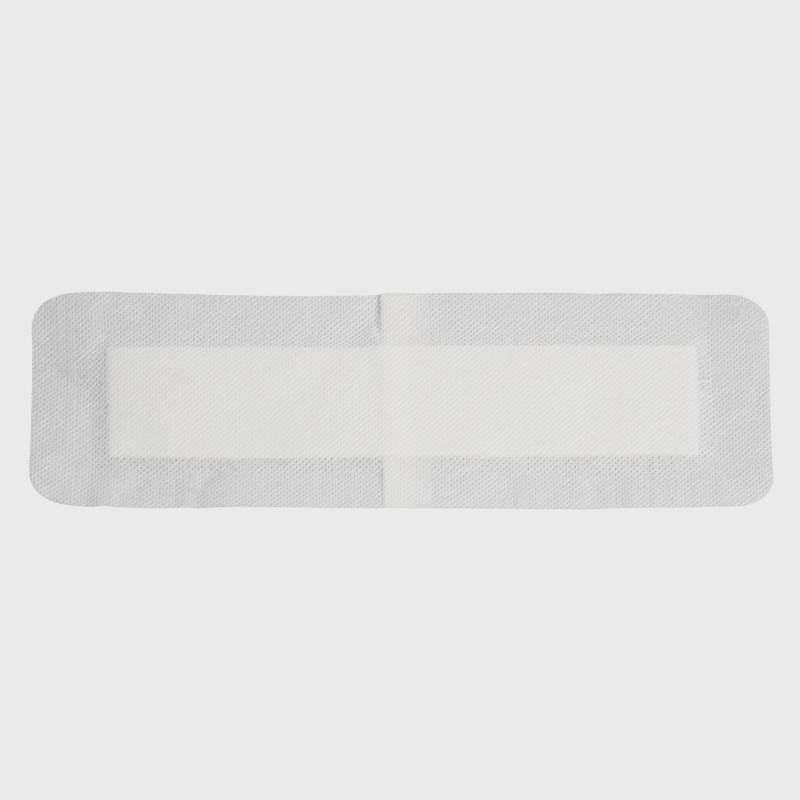
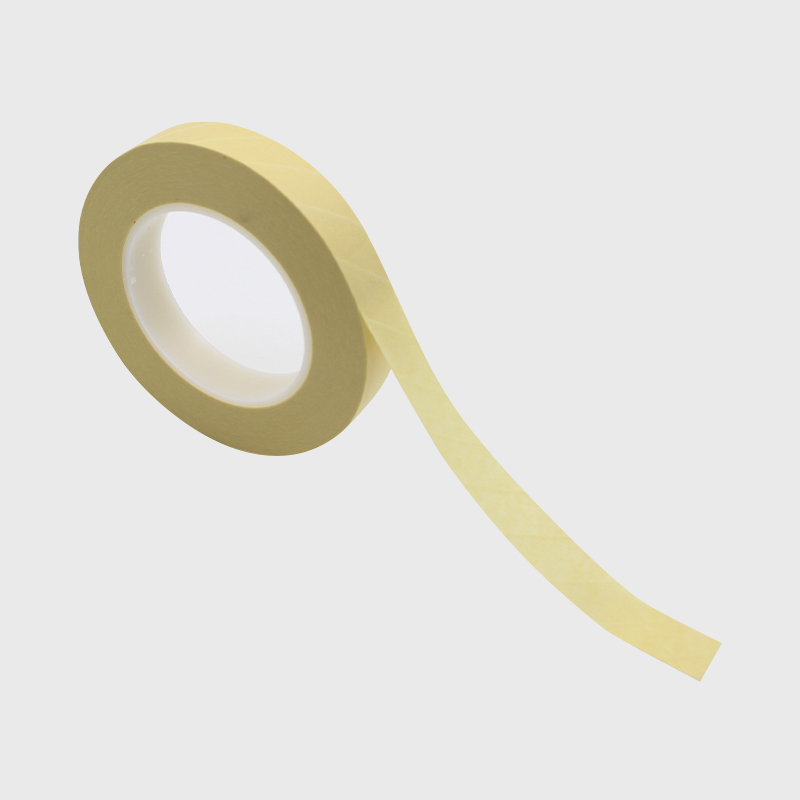
Chemical indicator card/tape: The color change visually reflects whether the sterilization temperature has been reached (such as 3M pressure steam indicator tape changes from white to black).
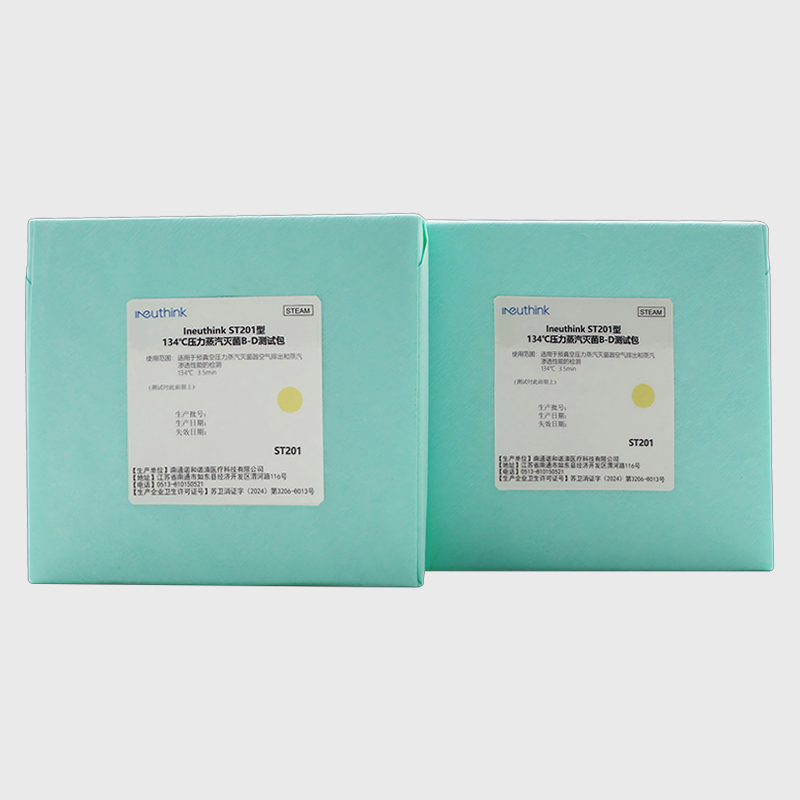
Bowie-Dick test: It is specifically used to detect the steam permeability of the pre-vacuum sterilizer to avoid "cold spots" caused by air residue.
(3) Biological monitoring
Geobacillus stearothermophilus is used as a biological indicator because of its strong heat resistance (it takes 121℃ for 15 minutes to kill). After sterilization, it is cultured for 48 hours. If there is no sterile growth, it indicates that the sterilization is successful.
Frequency requirement: Medical institutions need to monitor at least once a week. High-risk areas such as operating rooms are recommended to monitor every time.
3. Key factors affecting sterilization effect
Even if the equipment has excellent performance, improper operation may still lead to sterilization failure. The following factors need to be strictly controlled:
(1) Steam quality
Saturated pure steam (dryness ≥ 97%) must be used. Wet steam or steam containing air will reduce the heat transfer efficiency. It is recommended to equip a pure water generator to avoid mineral deposits clogging the pipes.
(2) Loading method
Wrong practices: Overfilling the sterilization chamber, overlapping instruments, and non-breathable packaging materials (such as ordinary plastic bags).
Correct specifications:
The volume of the items does not exceed 80% of the volume of the sterilization chamber;
The shaft joints of metal instruments must be opened, and fabrics should be placed upright;
Packaging should be done with medical crepe paper or Tyvek breathable bags.
(3) Equipment maintenance
Clean the sterilization chamber and drain filter daily to prevent impurities from affecting steam flow;
Calibrate the temperature/pressure sensor monthly;
Performance verification by a third party annually (such as EN 285 standard test).



 English
English Español
Español Français
Français










 CONTACT US
CONTACT US