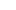Surgical Ligation Instruments And Consumables Manufacturers
With a building area of 20,310 square metres, the company has a class 100,000 purified production workshop, a class 10,000 microbiology testing room, a local class 100 physical and chemical laboratory, and a standardised storage system for raw materials and finished products.
Since the initial batch of products were launched in 2013, Eray has continuously enriched its product categories. Our products have covered protective masks, nursing consumables, sensory control consumables, surgical instruments, providing safe, efficient and environmentally friendly disposable medical solutions for medical institutions worldwide.
As a professional OEM Surgical Ligation Instruments Manufacturers and ODM Surgical Ligation Consumables Factory, The company has passed ISO 13485 and other quality system certifications, and some of its products have obtained CE certification and FDA filing permits, and has established long-term cooperative relationships with many domestic and foreign medical institutions and distributors.
-
Feb 27. 2026
Can Optical Trocars Reduce the Risk of Organ Injury?Optical Trocars Significantly Reduce Organ Injury Risk Yes, optical trocars can significantly reduce the risk of organ injury during laparoscopic surgery by allowing surgeons to visualize tissue layers in real time as the instrument passes through the abdominal wall. Unlike blin...
Read More -
Feb 20. 2026
What is an Optical Trocar and Why is it Essential in Medical Procedures?What is an Optical Trocar and Why is it Essential in Medical Procedures? An optical trocar is a specialized surgical instrument used primarily in minimally invasive procedures. It combines the functions of a trocar and a visual scope, allowing surgeons to create an access point ...
Read More -
Feb 13. 2026
What Are the Common Problems With Medical Trocars and How to Avoid Them?What Are the Most Common Problems With Medical Trocars? The most common problems with medical trocars include insertion injuries, gas leakage, dull blades, instability, and contamination risks. These issues can compromise surgical safety, increase operating time, and raise posto...
Read More
In minimally invasive surgery, ligation clip systems have become a key technology for closure of vessels and tubular tissues. This sophisticated system, comprised of a ligation clip, clip applier, and clip remover, offers surgeons a safe and efficient solution for vessel and tissue closure through its unique design and functionality.
The ligation clip, the core component of this system, is designed by integrating the best of materials science and biomechanics. These microclips are typically made of medical-grade titanium alloy or absorbable polymers, offering excellent biocompatibility and mechanical strength. The clip's V- or U-shaped design generates uniform closure pressure, ensuring secure closure of the vessel or tissue while avoiding excessive compression and tissue damage. A variety of clip sizes accommodate a wide range of closure requirements, from tiny vessels to larger tubular tissues, providing tremendous surgical flexibility.
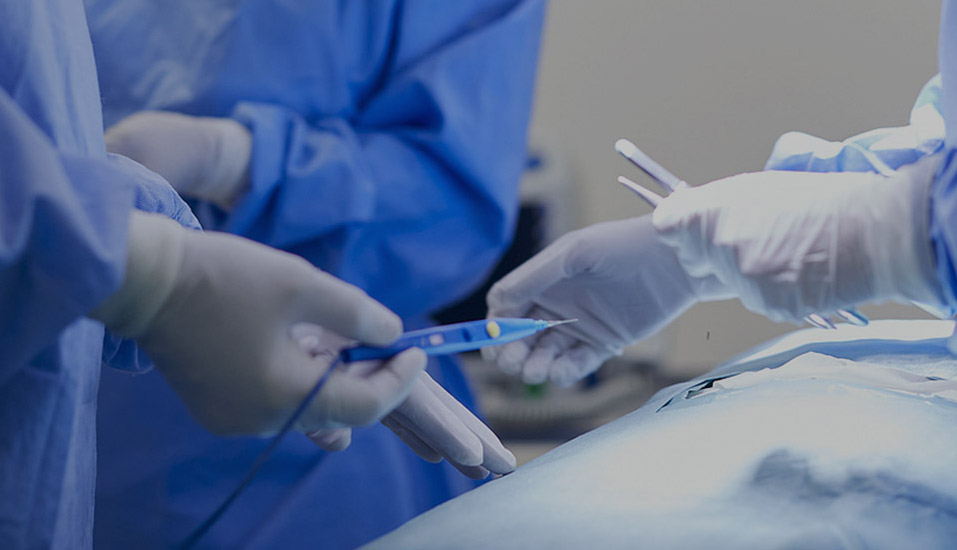
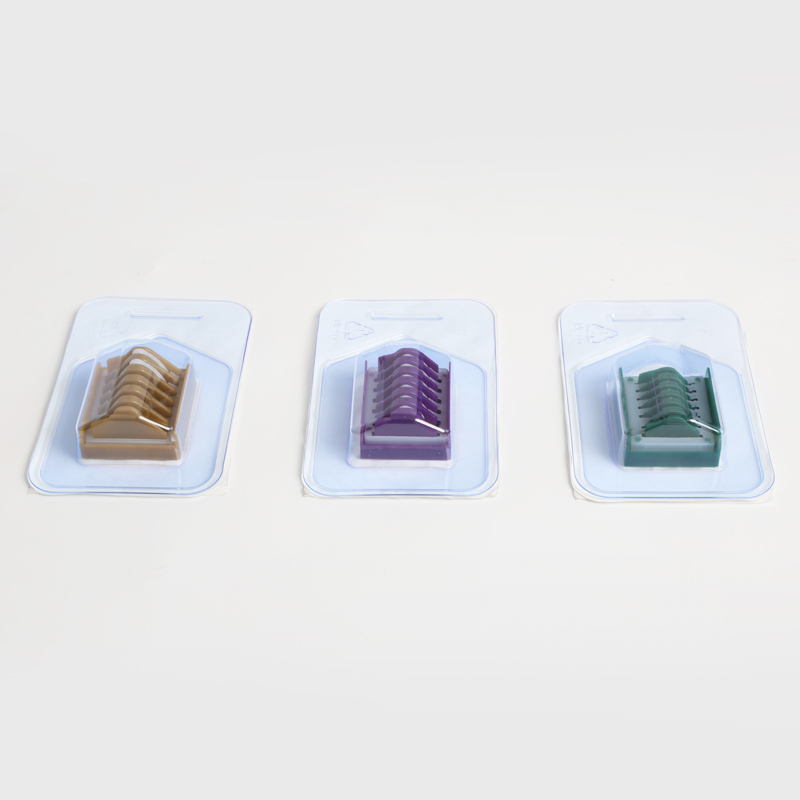
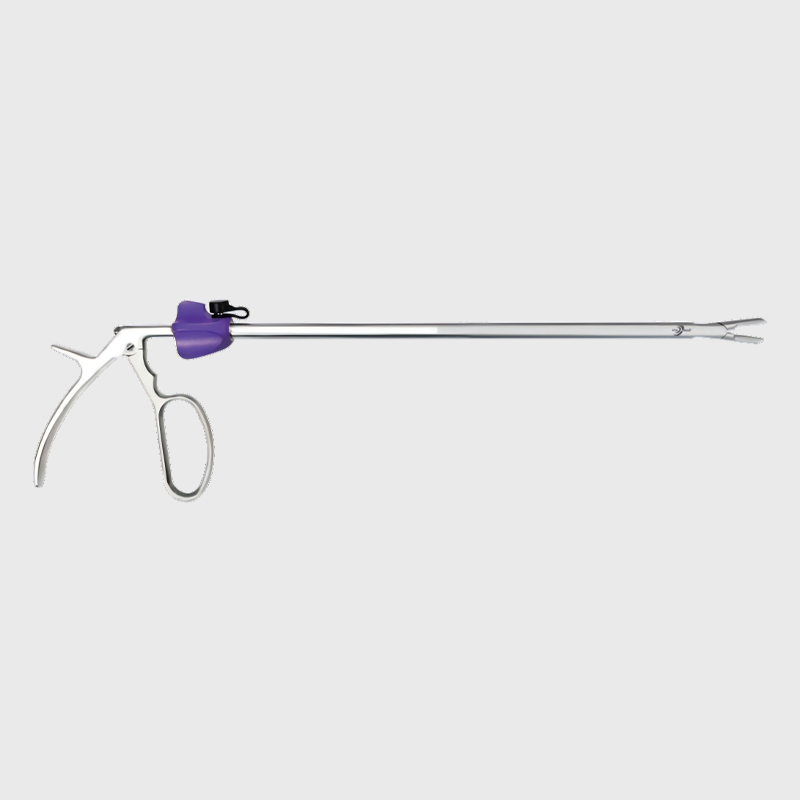
The clip applier, the clip delivery and release device, utilizes a slender shaft design, enabling access to deep surgical sites through small incisions during minimally invasive surgery. Its sophisticated mechanical structure allows for one-handed operation, enabling clip loading, positioning, and release with a simple movement of the handle. Some clip appliers also feature rotation and multi-angle adjustment, allowing surgeons to optimize their operating angles within a restricted surgical field of view. Disposable clip appliers often come preloaded with multiple clips, enabling continuous clip application without the need for reloading, improving surgical efficiency.
Clip removers securely grasp and remove placed clips without causing additional damage to surrounding tissue. The remover's precision jaw design ensures a secure grip on the clip, and its control mechanism allows the surgeon to precisely adjust the force required for removal, providing crucial margins for error during surgery.
During surgery, the surgeon uses the clip applier to precisely position the clip on the target vessel or tissue. Once the release mechanism is triggered, the clip securely closes the target area. This process takes only seconds, significantly improving surgical efficiency compared to traditional manual ligation. The clip's closing force is carefully calculated to ensure reliable closure without causing tissue damage. For areas requiring permanent closure, metal clips can remain in place for extended periods. For temporary closure, clips made of absorbable materials degrade after completing their mission.
Maintenance of ligation clips, clip appliers, and clip retrievers is crucial to ensuring the safety of laparoscopic surgery, requiring a rigorous maintenance procedure. Immediately after use, completely disassemble the instruments. Thoroughly clean the jaws, drive mechanism, and joints of the clip applier with a soft brush and a multi-enzyme detergent, paying particular attention to removing tissue residue from the clip groove and push rod. Ligation clips and clip retrievers should be cleaned separately, focusing on the contact surfaces with tissue to ensure they are free of blood and protein residue. After cleaning, thoroughly dry all lumens and crevices with a high-pressure air gun to prevent moisture retention and corrosion. Check the clamping force of the clip applier and the engagement accuracy of the clip retriever weekly, and test the push mechanism for smooth operation to ensure accurate clip release and retrieval with every operation.
Before sterilization, ensure that the instruments are completely dry. High-temperature-resistant components should be sterilized with autoclave steam at 134°C, while low-temperature plasma sterilization is recommended for precision drive mechanisms. During storage, separate instruments should be placed in dedicated instrument boxes to prevent damage from collisions. A functional test should be performed before each use to verify that the ligation clip is properly loaded and that the application and removal movements are smooth. Establish a complete usage record, record each maintenance and sterilization, and promptly replace instruments that are deformed, worn, or malfunctioning. Standardized maintenance and management not only prolongs the life of the instruments but also ensures the reliability of each ligation procedure, providing a strong guarantee for surgical safety.



 English
English Español
Español Français
Français























 CONTACT US
CONTACT US